Preventative breast cancer vaccine enters human trials
A promising breast cancer vaccine is entering human trials — and it’s designed to prevent the deadliest, most aggressive, hardest-to-treat form of the disease.
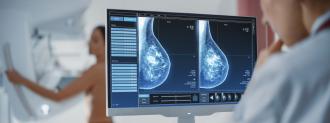
The challenge: When a person is diagnosed with breast cancer, their doctor will look at the cancer cells to see if they contain any of the three “receptor” proteins.
Each of these receptors binds to a specific hormone or protein (estrogen, progesterone, or human epidermal growth factor) to fuel the cancer’s growth. Knowing which are present on cancer cells helps doctors determine which treatments to administer.
The five-year survival rate for triple-negative breast cancer is 75%, compared to 90% for all breast cancers.
But about 15% of cancer patients have what’s known as “triple-negative breast cancer,” meaning the cancer cells don’t have any of the receptors, which severely limits treatment options.
This type of cancer also spreads quicker, is harder to detect early, and has high recurrence rates. As a result, triple-negative breast cancer is the most deadly type, with almost 25% of patients dying within five years of diagnosis (the rate for all types of breast cancer is 10%).
The breast cancer vaccine: Instead of focusing on treating triple-negative breast cancer, Cleveland Clinic scientists want to prevent it — and after two decades of research, they think they have a vaccine that might do the trick.
Their breast cancer vaccine targets a milk protein called “α-lactalbumin,” which can be found in breast cancer cells. It’s in particularly high levels in triple-negative breast cancer cells.
“The general idea behind the vaccine is that … we can stimulate the immune system to attack cells that make that protein,” principal investigator Thomas Budd told New Atlas.
The trial: The breast cancer vaccine has already demonstrated an ability to prevent the appearance and growth of tumors in animals, and the Cleveland Clinic is now launching a phase 1 trial in humans.
“The long-term objective is to determine if this vaccine can prevent breast cancer before it occurs.”
Vincent Tuohy
This trial will include 18 to 24 people diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer in the past three years. They will all be tumor-free, but at high risk of recurrence due to factors such as their genetics or family history. Each will receive three shots delivered two weeks apart.
The purpose of this trial will be to determine the maximum tolerable dosage of the breast cancer vaccine and to maximize its immune response. It is expected to wrap up around September 2022.
Looking ahead: If all goes well with the phase 1 trial, the next step will be a trial of patients who have never had triple-negative breast cancer, but are at high-risk (typically due to genetic mutations) and have voluntarily undergone bilateral mastectomies.
“The long-term objective of this research is to determine if this vaccine can prevent breast cancer before it occurs, particularly the more aggressive forms of this disease that predominate in high-risk women,” Vincent Tuohy, the shot’s primary inventor, said.
The cold water: It could be another decade before we know whether the breast cancer vaccine works, as the researchers will need some trial participants to actually develop breast cancer to determine its efficacy.
“It will take years to develop and test something like this because it takes years to see whether you’re preventing a cancer that may occur over a person’s lifetime,” Budd said. “But we have to start somewhere — and we’re really excited to take our first step.”
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].