NASA shares colorful “postcard” of Mars’ surface
During its 11 years on the Red Planet, NASA’s Curiosity rover has proven to be quite the photographer, snapping stunning photographs of a “Martian flower,” a feather-shaped iridescent cloud, and a strange book-like rock.
Now, NASA has combined and colorized two Curiosity panoramas to create a gorgeous “postcard” of the Martian landscape.
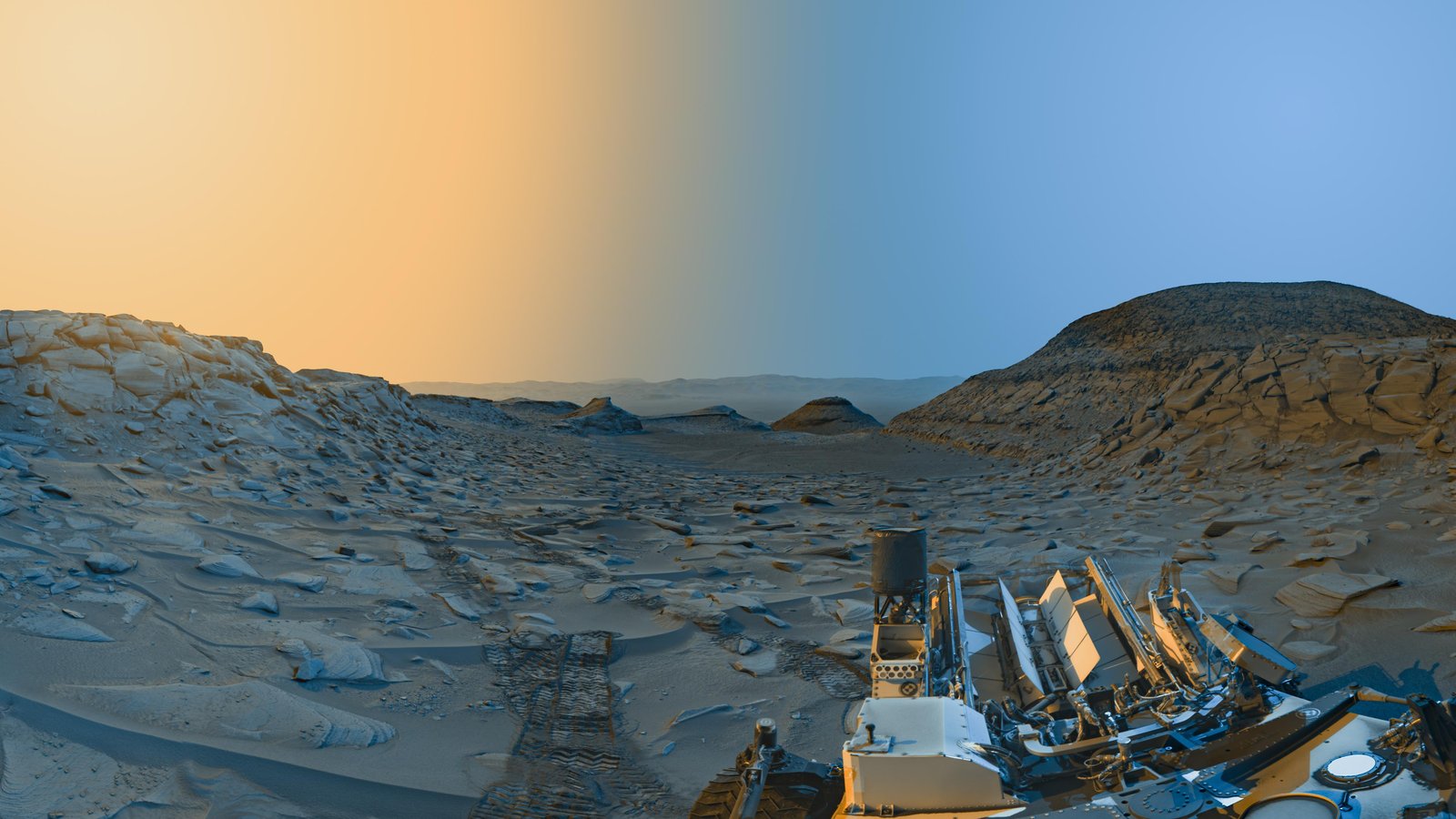

At 9:20 am on April 8, the Curiosity rover spent about 7.5 minutes taking multiple photographs of Mars’ Marker Band Valley. Without moving from its location in the foothills of Mount Sharp, it photographed the same region again at 3:40 pm.
After the photographs were sent to Earth, Curiosity engineer Doug Ellison stitched together five photos from each session to create a morning panorama (with the sun on the right side of the photograph) and an evening panorama (with the sun on the left).

Ellison then combined the images, and thanks to the opposing “suns,” the resulting composite featured dramatic shadows.
“Capturing two times of day provides dark shadows because the lighting is coming in from the left and the right, like you might have on a stage — but instead of stage lights, we’re relying on the sun,” he explained.
The fact that it was winter when the Curiosity rover took the photos enhanced the effect — according to NASA, that’s the season when shadows on Mars’ surface are “deepest and darkest,” due to minimal dust in the planet’s atmosphere
Finally, Ellison added blue to the parts of the photograph taken in the morning and yellow to the parts from the afternoon, creating an artistic interpretation of the scene.
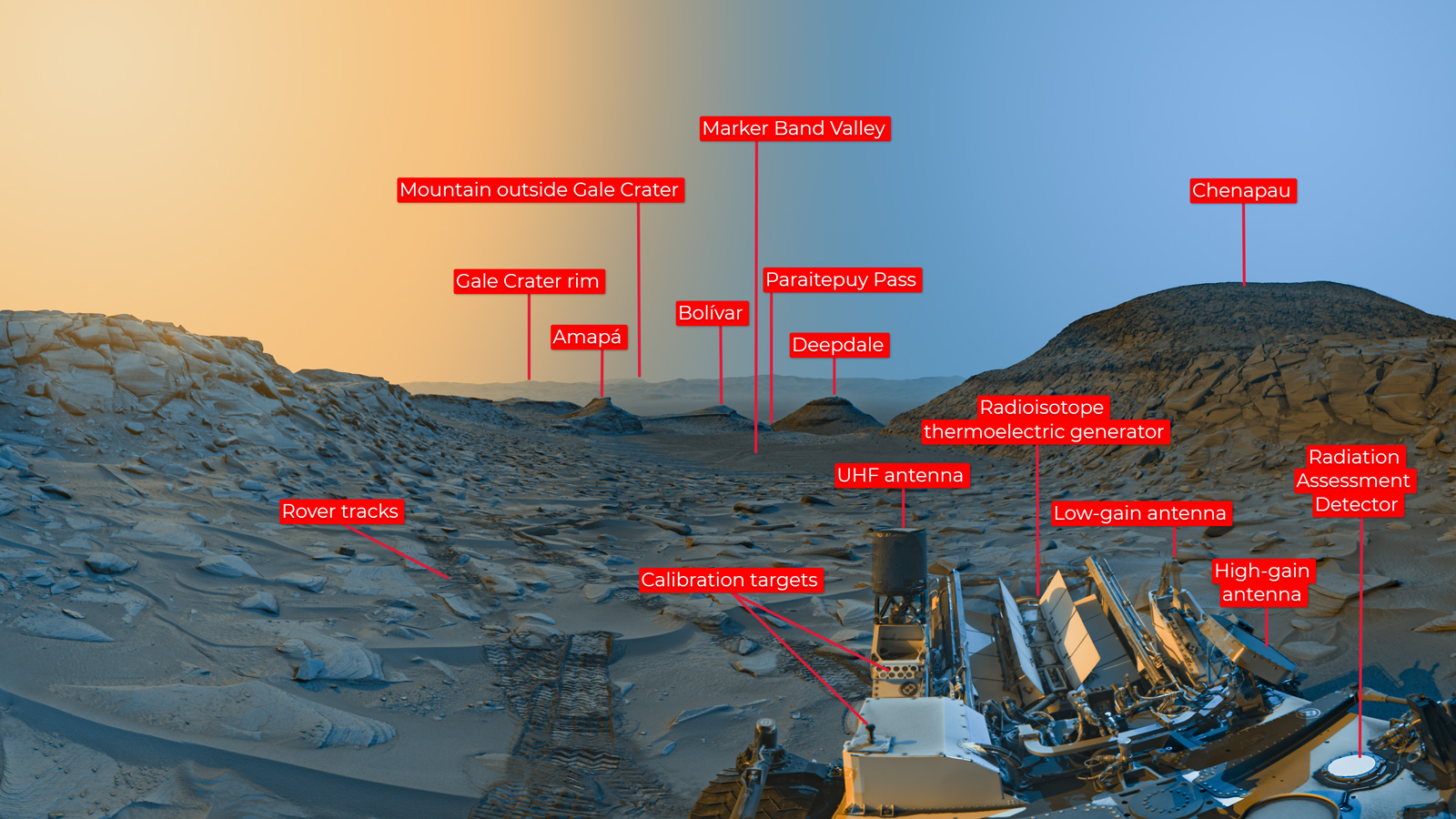
In addition to that “clean” image, NASA has also released one identifying various features across the Martian landscape, including a mountain more than 75 miles away, as well as parts of the Curiosity rover that are visible in the photo’s foreground.
This isn’t Curiosity’s first postcard. In 2021, NASA shared another one in which blue, yellow, and green were added to a composite of morning and afternoon photographs of Mars’ surface.
The new postcard might not be Curiosity’s last, either — in April, NASA made a major update to the rover’s software, implementing 180 improvements that should help keep it operational for several more years to come.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].




