Startup plants first GMO trees designed for carbon removal
To combat climate change, a biotech startup has genetically engineered trees to be better at pulling carbon from the air — and after years of research, it’s finally ready to put some of its GMO trees in the ground.
The challenge: Dramatically cutting our greenhouse gas emissions likely won’t be enough to prevent damaging climate warming — we’re also going to need to capture and sequester some of the carbon that’s already in the air.
Trees are natural carbon sinks — they pull CO2 from the air through photosynthesis and then store it in their roots, branches, and leaves.
Typically, the bigger a tree is, the more carbon it can store, but time also matters — it can take decades for a tree to grow from a seedling to full height, and we need to capture as much carbon as we can as soon as possible.
The genetic tweaks are designed to make the trees more efficient at photosynthesis.
GMO trees: Since 2019, California’s Living Carbon has been exploring ways to use genetic engineering to make trees a better weapon in the fight against climate change.
They’ve now landed on their first product: a fast-growing hybrid poplar tree that can reportedly capture more carbon than its unmodified counterparts. The company plans to plant 4 million of these GMO trees in 2023, starting with 60,000 seedlings in Georgia and Pennsylvania in February 2023.
How it works: According to a paper shared on the preprint server bioRXiv, Living Carbon created their GMO trees by using a bacterium to insert genes from squash and green algae into hybrid poplars.
These tweaks were designed to make the trees more efficient at photosynthesis, and they seemed to work — during a five-month-long trial in a controlled environment, the modified poplars grew faster than unmodified trees, packing on 53% more above-ground biomass.
This is equivalent to capturing about 27% more carbon, according to co-founder and CEO Maddie Hall.
“Beyond additional carbon captured, we have also seen a 97% survival rate of our seedlings on abandoned mineland planting projects, and an increased resilience to hot temperatures,” she added.
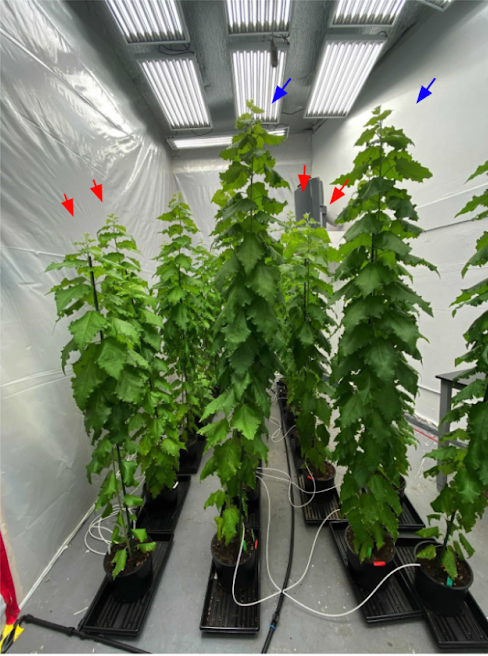

The caveats: The results of the preprint paper and other planting projects have not yet been peer-reviewed, and we still have no indication how well the GMO trees will grow under real-world conditions for long periods of time.
The seedlings Living Carbon is now planting weren’t created in the same way as the ones it studied for the paper, either — instead of using bacteria to insert the genes, it used a device called a “gene gun,” as this eliminated the need to involve the US Department of Agriculture.
Looking ahead: Living Carbon’s CTO Patrick Mellor told New Scientist that the company has tested trees made using the gene gun in greenhouses and found that they had growth rates similar to the ones modified using bacteria.
The only way to find out how the GMO trees will grow longterm in the wild, meanwhile, is to actually grow them, and the company’s current goal is to get more than four million seedlings in the ground over the next year.
It already has the funding needed to produce and plant up to 5 million GMO trees, which can be purchased by individuals and companies eager to support the deployment of “supertrees” in the battle against climate change.
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at [email protected].